4-Aminobenzoic acid CAS 150-13-0Specification:
| Item | Specifications |
| Appearance | Light yellow or gray white to Off-white powder |
| Melting range | 186~189℃ |
| Assay | ≥98.5% |
| Characters | White or light yellow crystal or crystalline powder without smell |
| Loss on drying | Not more than 0.2% |
| Residue on ignition | Not more than 0.1% |
| Assay | 98.0~102.0% |
| Aniline andP-toluidine | Aniline≤10ppm |
| P-toluidine≤10ppm | |
| Appearance | White to off-white crystalline powder |
| Assay | ≥99.0% |
| Melting point | 186-189℃ |
| Loss on drying | ≤0.5% |
| Organic impurities | Nitrobenzoic acid |
| Benzocaine<0.2% | |
| Any unspecified impurity≤0.1% | |
| Total impurities<0.5% | |
| Identification | IR should comply with the reference
standard spectrum. Solution main peak retention time should be consist with standard solution main peak retention time |
| structural | 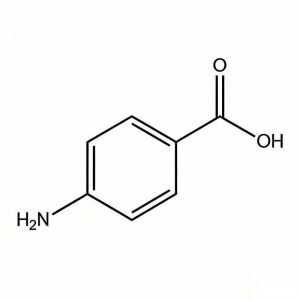 |
Application Usage:
Introduction
p-Aminobenzoic acid (PABA) is also a vital fine chemical raw material. In the pharmaceutical sector, it acts as a key intermediate for synthesizing tranexamic acid (a hemostatic agent) and folic acid (a hematinic), and manufacturers use it to produce drugs that treat rickets, rheumatism, arthritis, and tuberculosis.cosmetics industry, it serves as an important intermediate for human sunscreens and hair-growth products. In organic chemical manufacturing, producers rely on it to make various ester products—these products function as resin modifiers and special intermediates in the synthesis of reactive dyes and azo dyes.
Uses of Para-Aminobenzoic Acid
Chemical properties
Package and Shipping:
Store in a well-ventilated warehouse at low temperature and keep dry,25kg/bag .
Storage:
6-8t/month



 GET FREE SAMPLE
GET FREE SAMPLE