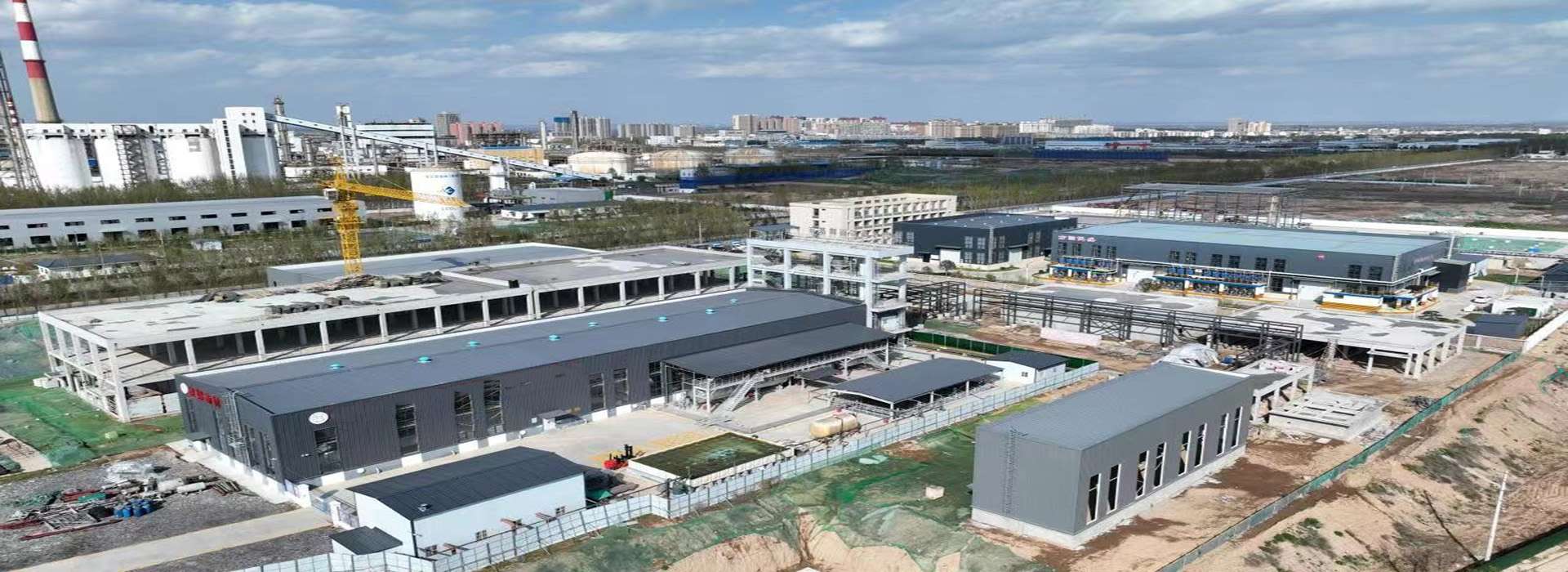






ZHC Chemical Co.,Ltd. Is owned by RUIJIA Group, was established in 2011 .The headquartered located in the beautiful Spring city Jinan. ZHC Chemical is large-scale manufacturing enterprise integrating R&D, produce and sales. The company competitive product is pharmaceutical intermediates (especially guanidine & Ethyleneurea Series), In recent years, the company has made a major breakthrough in biological buffers ,additive agents, and cosmetic raw materials etc.
“ZHC” enterprise idea of development: Zeal、Heart、 Care for every customers and every details !
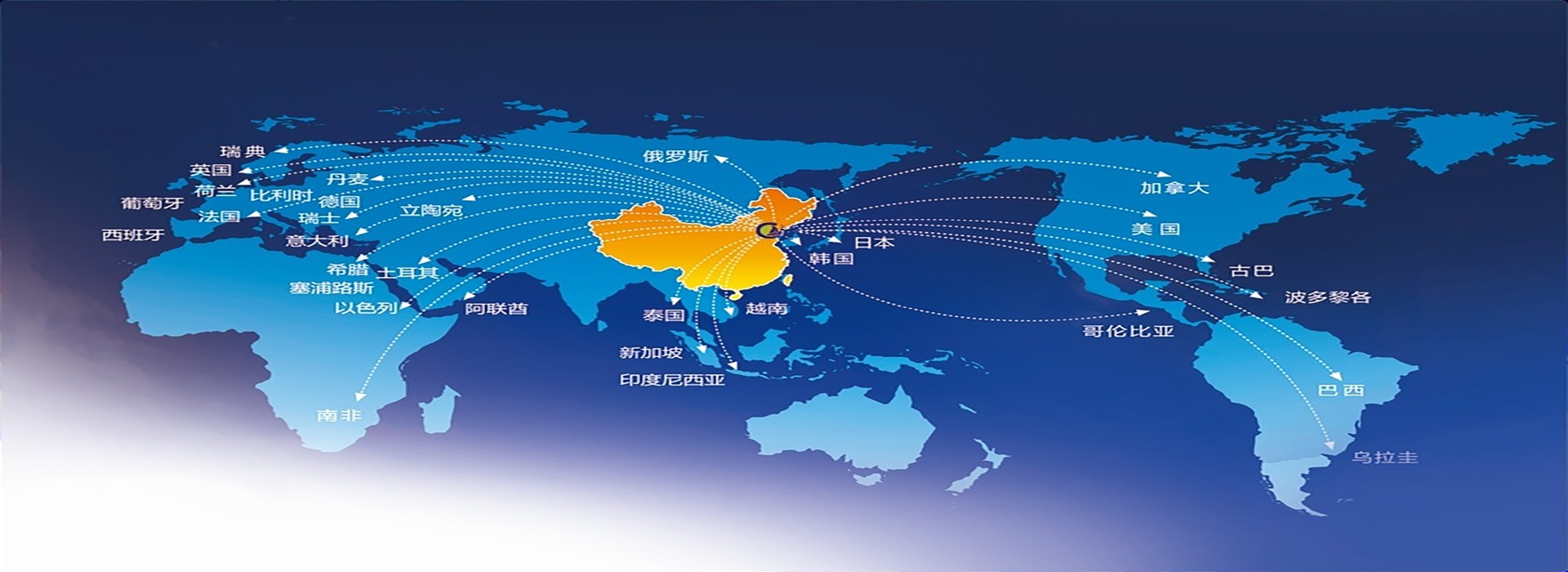
We sincerely welcome friends domestic and abroad to discuss cooperation !
YEARS EXPORT EXPERIENCES
COUNTRIES
customer
Online all 7days in A Week
04
2026 - 02
1,4-Butane sultone CAS 1633-83-6In the era of rapid energy transition and electric vehicle (EV) expansion, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) serve as core energy storage components. Their performance, safety, and cycle life directly determine the market competitiveness of end-user products. As the “blood” of the battery, the electrolyte plays a vital role in conducting ions and isolating electrodes. To overcome the limitations of traditional carbonate-based electrolytes in high-voltage and high-energy-density systems, the research into functional additives is paramount. Among these, 1,4-Butane Sultone (1,4-BS) has emerged as a high-efficiency film-forming additive, demonstrating unique value and broad application prospects in optimizing battery electrolytes. 1. Molecular Mechanism and Interface Formation 1,4-Butane Sultone is a cyclic sulfonate ester compound. Its molecular structure, characterized by the sulfonyl group and cyclic lactone configuration, imparts specific electrochemical activity. When added in precise concentrations (typically 0.5%–5%) to standard electrolytes composed of lithium salts and organic solvents, it undergoes preferential reductive decomposition on the graphite anode surface during the initial charging cycle. This process, occurring before the solvent molecules react, forms a uniform, dense, and ionically conductive Solid Electrolyte Interphase (SEI). As the “gatekeeper” of battery performance, the quality of this in-situ generated SEI film directly influences: Coulombic Efficiency: Reducing initial capacity loss. Cycling Stability: Extending the lifespan of the cell. Rate Capability: Enhancing power delivery performance. Low-Temperature Performance: Ensuring reliability in cold environments. The SEI layer formed by 1,4-BS is rich in organic lithium sulfonates, offering a more stable structure that effectively inhibits continuous electrolyte decomposition and graphite exfoliation. This is particularly critical for enhancing the first-cycle efficiency and long-term stability of high-capacity silicon-carbon anodes or high-voltage cathode systems. 2. Outlook in High-Voltage and High-Energy-Density Applications As market demand for energy density increases, cathode materials are evolving toward high-nickel (e.g., NCM811, NCA) and high-voltage (e.g., $LiCoO_2$, lithium-rich manganese-based) chemistries, with…
03
2026 - 02
Sodium thioglycolate(CAS 367-51-1) is a white crystal. It is hygroscopic and has a slight special odor. Its melting point is above 300°C. It is easily soluble in water and slightly soluble in ethanol. It changes color when exposed to air or in contact with iron. If it turns yellow or black, it has deteriorated and must not be used. 1.Sodium thioglycolate Physical and Chemical Profile Sodium Thioglycolate is a highly functional chemical compound recognized for its versatility as a reducing agent and chelator. Appearance: White crystalline substance. Key Traits: It is significantly hygroscopic (readily absorbs moisture) and possesses a mild, characteristic odor. Stability: Features a melting point above 300°C. Solubility: It shows excellent solubility in water and is slightly soluble in ethanol. Quality Indicator: The compound is chemically active and prone to discoloration (turning yellow or black) when exposed to air or in contact with iron. Discoloration is a critical indicator of degradation; degraded material should not be used. 2. Key Industrial Applications A. Advanced Metal Surface Treatment Sodium Thioglycolate is a primary component in high-efficiency surface treatment agents. Its superior complexing and reducing properties allow it to form a dense protective film on metal surfaces. Performance: Enhances corrosion resistance and surface adhesion. Results: Metal components treated with this compound show over a 30% improvement in salt spray test durability. Target Industries: Ideal for automotive parts and mechanical equipment manufacturing. B. Heavy Metal Removal in Wastewater Treatment In environmental engineering, Sodium Thioglycolate is used to solve the challenge of heavy metal contamination. The sulfhydryl (-SH) groups in its structure specifically chelate with heavy metal ions like Lead (Pb), Mercury (Hg), and Cadmium (Cd). Mechanism: It creates stable, water-insoluble precipitates through a chelation-flocculation synergistic effect. Efficiency: Achieves removal rates of over 98% for heavy metal ions and significantly reduces Chemical Oxygen…
02
2026 - 02
1,4-Butane Sultone (Chemical Formula: $C_4H_6O_3S$) is a critical sulfur-containing heterocyclic compound. Structurally, it is a four-membered ring lactone formed by a butane chain connected via a sulfonic acid group and an oxygen atom. This unique strained-ring structure—combined with an active sulfonate bond—provides the high reactivity necessary for advanced chemical synthesis.Technical Specifications & Core ChemistryPhysical State: Typically a colorless to pale yellow liquid or a low-melting-point solid.Solubility: Highly soluble in polar organic solvents like DMSO and DMF.Stability: It is hygroscopic and tends to undergo ring-opening reactions when exposed to water.Reactivity: The core value of 1,4-Butane Sultone lies in its electrophilic sulfonate group. It reacts readily with nucleophiles such as amines, alcohols, thiols, and carbanions through ring-opening addition, allowing for the precise introduction of sulfonic acid functional groups into various molecules. 1,4-Butane Sultone Key Industrial Applications 1. Synthesis of High-Performance Surfactants One of the most vital uses for 1,4-Butane Sultone is its reaction with primary or secondary amines. This process yields betaine-type amphoteric surfactants (N-substituted butane sulfonic acid inner salts). Properties: These products feature both quaternary ammonium cations and sulfonic acid anions. Benefits: They offer excellent surface activity, low irritation, high biocompatibility, and resistance to hard water. Use Cases: Premium personal care products (shampoos, body washes), cosmetics, and specialized industrial cleaners. 2. Advanced Polymer Functionalization In polymer science, 1,4-Butane Sultone serves as a high-value modifying monomer. By reacting with active sites like amino or hydroxyl groups, it introduces sulfonic acid groups into polymer side chains or end groups. Proton Exchange Membranes (PEM): It is essential for modifying engineering plastics (e.g., polyaryletherketone, polyimide) used in fuel cells. Performance Impact: It enhances hydrophilicity, ionic conductivity, and high-temperature tolerance while reducing methanol permeability. 3. Battery Technology & Electrochemical Additives Recently, 1,4-Butane Sultone has become a focal point in the development of Lithium-ion batteries and supercapacitors….
28
2026 - 01
Sodium thioglycolate (CAS 367-51-1), a commonly used chemical in the chemical industry and daily life sectors, has its potential hazards following human exposure and the corresponding protective technologies as the core issues for safeguarding occupational health and public safety. Based on the exposure standards of the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the research data of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), this paper systematically analyzes the hazards of different exposure routes to the human body and provides feasible protective technical solutions, integrating scientific rigor and practical operability. 1.Sodium thioglycolate Overview of Environmental Impact Sodium Thioglycolate is widely used in chemical synthesis, laboratory reagents, and personal care manufacturing. However, its lifecycle—from production to disposal—presents significant ecological risks if not managed through rigorous safety protocols. Due to its chemical stability, this compound has a natural half-life of 14 to 21 days in aquatic environments, making it resistant to rapid biodegradation and prone to accumulation in sediment. 2.Ecological Toxicity Data (EPA & ISO Standards) According to data aligned with U.S. EPA Ecotoxicology standards and ISO 10993 assessment methods, Sodium Thioglycolate exhibits specific toxicity levels across different ecosystems: A. Aquatic Ecosystems The compound is highly hazardous to aquatic life even at low concentrations: Freshwater Fish (e.g., Zebrafish): Concentrations ≥0.5 mg/L cause gill damage and respiratory distress. The 96-hour Median Lethal Concentration (LC50) is documented at 2.3 mg/L. Aquatic Plants (e.g., Duckweed): The EC50 (Half Maximal Effective Concentration) for growth inhibition is 1.8 mg/L, which can disrupt the entire aquatic food chain over long-term exposure. B. Soil and Agriculture In soil, Sodium Thioglycolate binds with metal ions to form insoluble compounds, reducing soil permeability and hindering root development: Crop Impact: Soil concentrations exceeding 5 mg/kg reduce the germination rates of staples…
06
2026 - 01
Orotic acid is an organic compound once mistakenly classified as vitamin B13. Subsequent extensive scientific research has confirmed that it does not belong to the vitamin family. However, due to its unique biological activity, orotic acid continues to hold irreplaceable value in the fields of medicine, health, and the chemical industry. Orotic acid-based products are widely recognized and studied by research institutions, the medical community, and the chemical industry for their core advantages: high efficacy, low side effects, minimal kidney irritation, and low residual accumulation in the body. Synthesis From a synthetic pathway perspective, the industrial production of orotic acid primarily employs chemical synthesis methods. The core steps, validated by scientific research, demonstrate stability and reproducibility. Starting with diethyl oxalate, it undergoes a condensation reaction with acetic acid, followed by a cyclization reaction with urea to form 5-ethoxycarbonylmethylene hydantoin. The molecular structure is then optimized via a ring-expansion reaction, and finally, high-purity orotic acid is obtained through acid precipitation and purification processes. Alternatively, orotic acid can be extracted from whey, a by-product of the cheese industry. Whey contains 50% of the nutritional components of the original milk. Through separation and purification processes, natural orotic acid can be obtained. Both synthetic routes comply with chemical industry production standards, and the purity and safety of the products have been verified by relevant testing and certification. Role and Functions The application scope of orotic acid continues to expand. Since the 1960s, it has been used clinically to treat jaundice and general liver dysfunction. Today, it remains an important substance for liver protection and repair. Modern pharmacological studies indicate that orotic acid can promote the repair and regeneration of liver cells, regulate the activity of liver metabolic enzymes, and has clear auxiliary therapeutic effects for patients with chronic liver diseases such as chronic hepatitis…
05
2026 - 01
Basic Properties and Chemical Structure of Piperazine Piperazine (CAS 110-85-0) is an indispensable basic nitrogen-containing heterocyclic compound in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Its unique chemical structure combines rigidity with flexibility, and its dual amine functional groups offer rich possibilities for structural modifications and functional expansions. This versatility enables to play a crucial role in various specialized fields such as drug innovation, advanced material synthesis, and environmental remediation. The research, development, and industrialization of related technologies continue to advance at a rapid pace. Applications of Piperazine in the Pharmaceutical Field The structural advantages of piperazine provide core solutions for optimizing drug performance. Its rigid six-membered ring structure effectively locks the active conformation of drug molecules, enhancing their binding specificity to target proteins and thereby improving bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. Data from multiple preclinical studies indicate that introducing a piperazine ring into antihistamine drugs increases their selective binding to H1 receptors by 35%, effectively reducing central nervous system side effects such as drowsiness. In antibacterial drug design, the incorporation of piperazine side chains improves the lipophilicity of drugs, enhances cell membrane permeability, and significantly increases inhibitory activity against drug-resistant strains. Notably, in the field of anticancer drugs, piperazine-modified prodrugs utilize pH-sensitive properties to rapidly activate in the acidic environment of tumor tissues. This leads to a threefold increase in drug concentration at the lesion site compared to conventional formulations while reducing damage to normal organs such as the heart and liver. Additionally, is widely used in the synthesis of antiparasitic and psychiatric drugs, making it one of the most extensively applied heterocyclic skeletons in medicinal chemistry. Applications of Piperazine in the Chemical Industry The high-performance characteristics of piperazine drive technological upgrades in multiple advanced fields. In high-temperature-resistant materials, polyamide-imide (PAI) resins synthesized using as a monomer exhibit a heat deflection temperature…
Years of industry experience, technical expertise, and professional team collaboration to jointly create
Ensure product quality, cooperate with various mainstream chemical factories, and provide high-quality products;
We have professional sales consultants to provide one-on-one service and timely guidance to customers
We provide various chemical raw material products to better meet customer needs
Strong Sourcing System + Large Clients Volume
Provide customers with more professional, fast and safe transportation methods

If you have any questions or need help, please contact us through the following ways:

+86 15650010696

+86 15650010696

info@zhcchem.com

No.60 North Gongye Road, Licheng District,Jinan City, China. PC.250100.

If you have any questions or need help, please contact us through the
following ways:

+86 15650010696

+86 15650010696

info@zhcchem.com

No.60 North Gongye Road, Licheng District,Jinan City, China. PC.